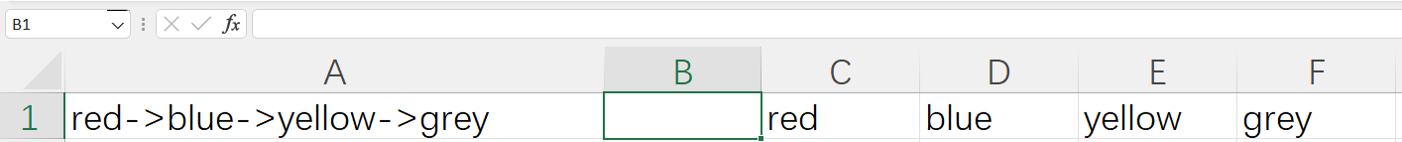
=spl("=?.split(""->"")",A1)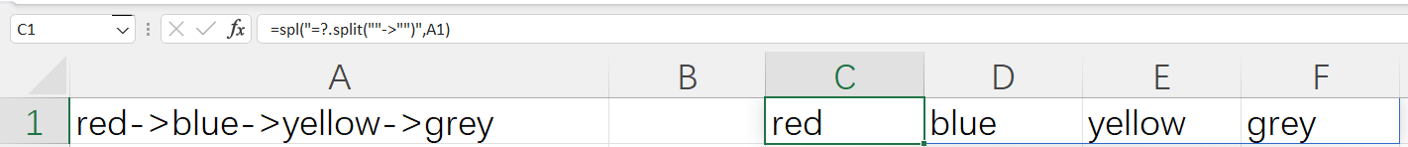
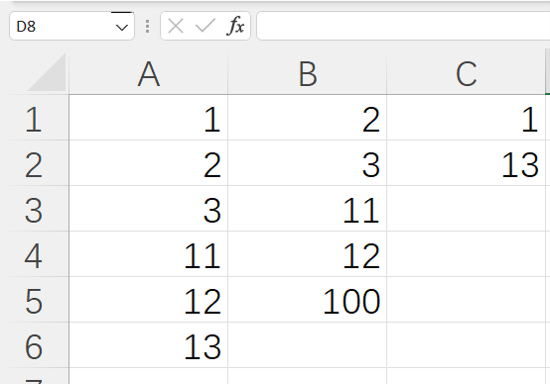
=spl("=?1\?2",A1:A6,B1:B5)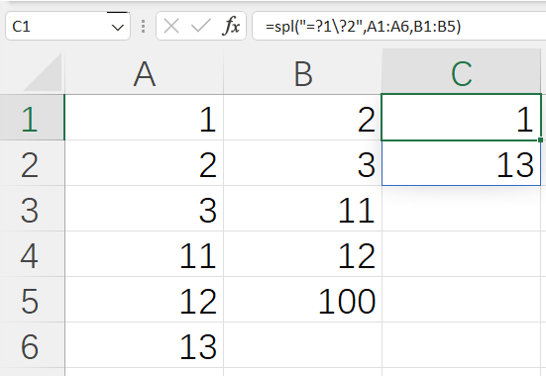
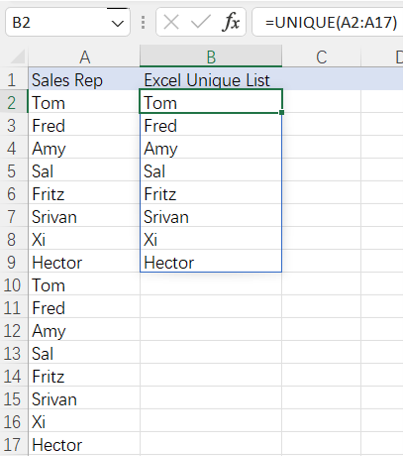
=spl("=?.id@u()",A2:A17)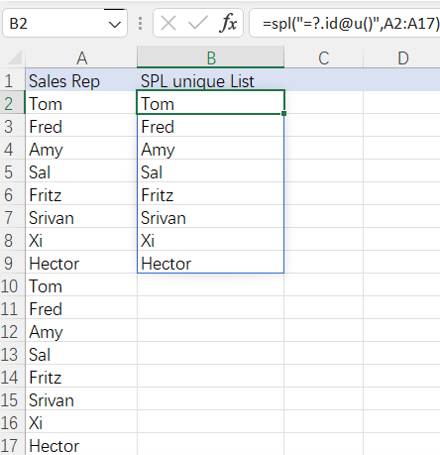
More about SPL id function:
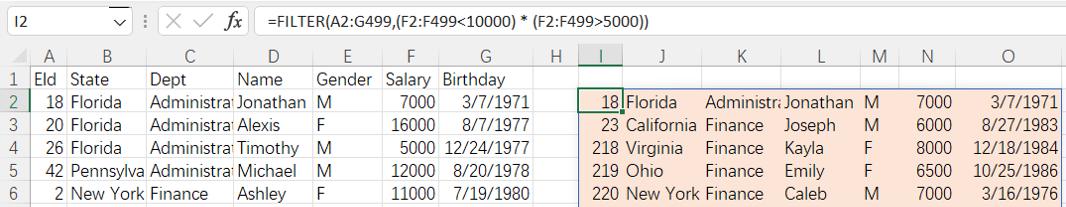
=spl("=E(?).select(Salary>5000 && Salary< 10000 && like(Name,""*Jo*""))",A1:G499)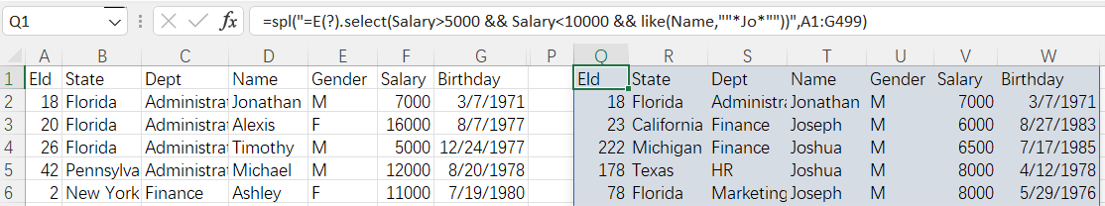
More about SPL select function:
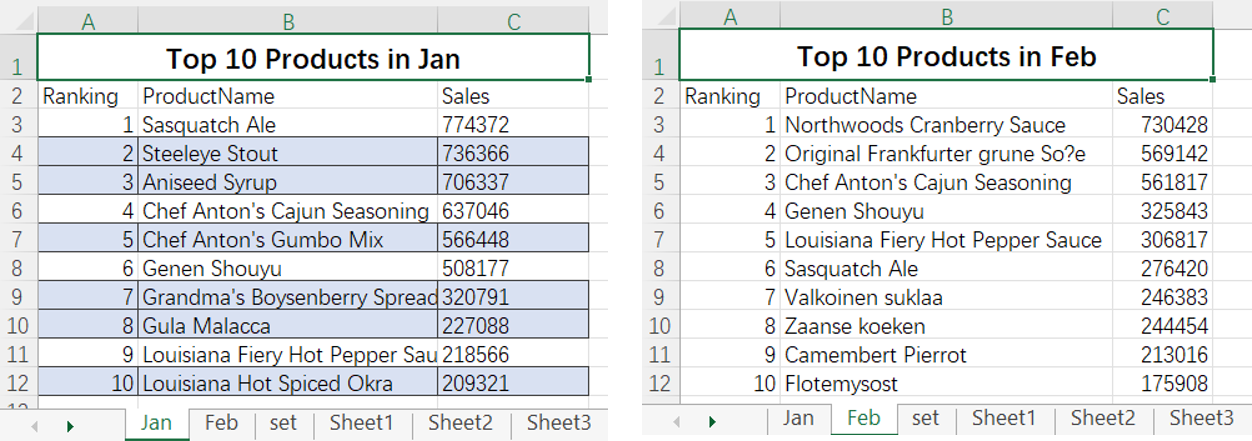
=spl("=[E(?1),E(?2)].merge@od(ProductName)",Jan!A2:C12,Feb!A2:C12)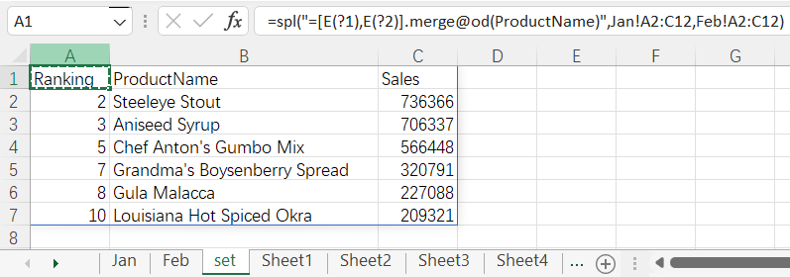
More about SPL merge:
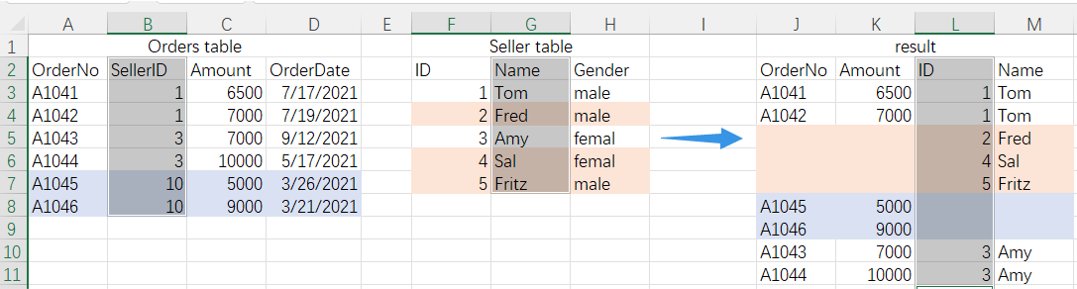
=spl("=join@f(E(?1),SellerID;E(?2),ID).new(_1.OrderNo,_1.Amount,_2.ID,_2.Name)",A2:D8,F2:H7)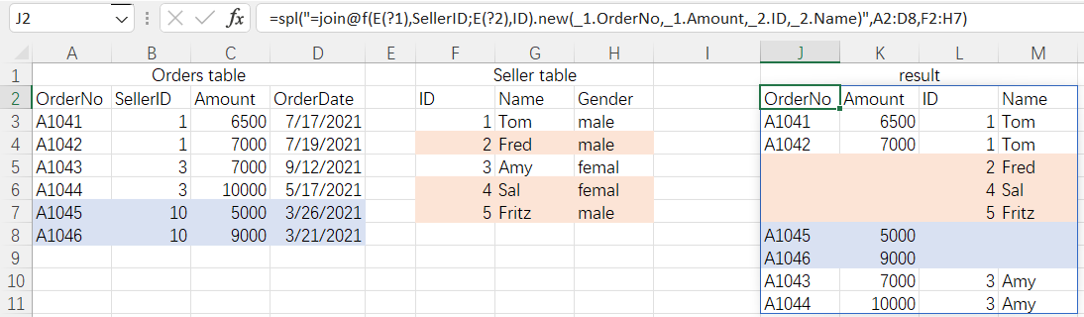
More about SPL join:
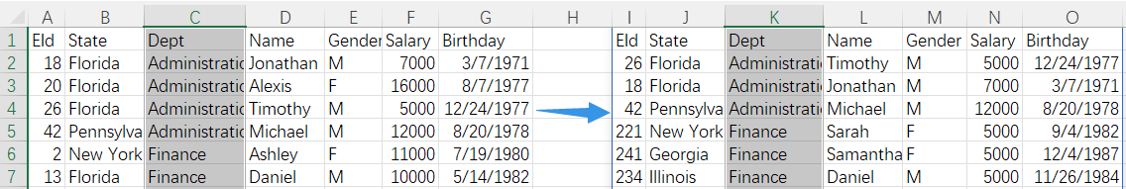
=spl("=E(?1).group(Dept).conj(~.top(3;Salary))",A1:G499)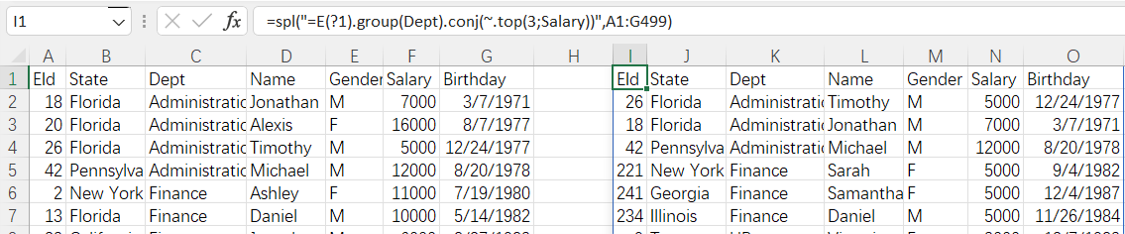
More about SPL top function: