Programming Language
that can be learned by non-professionals
Toolkits
for desktop data analysis and processing
Simple operation, rich functions
Tedious batch and repetitive tasks
Insufficient support for complex operations
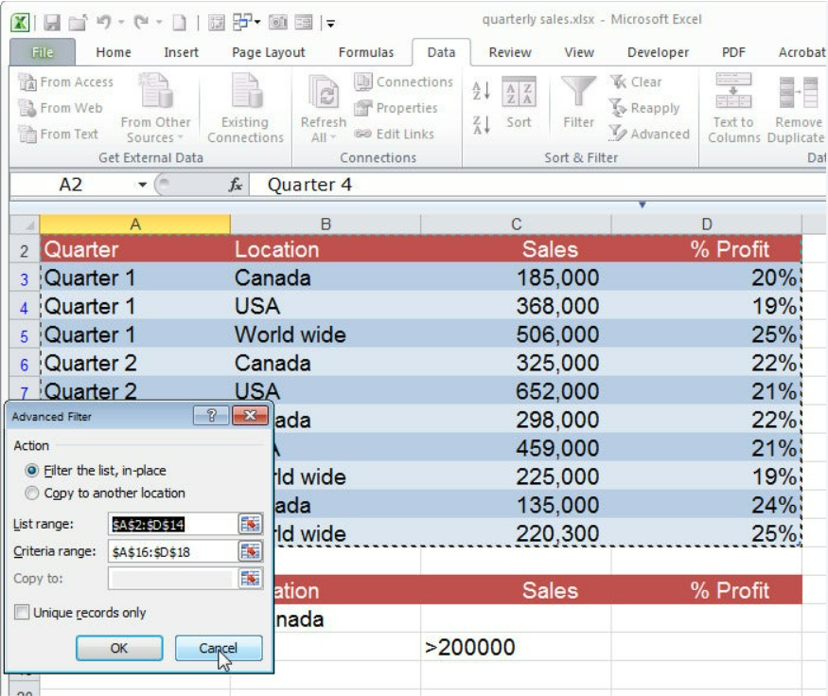
Simple to use, smooth and beautiful interface
Single calculation, can only do rigid multidimensional analysis

Full programming capabilities, naturally built in Excel
Poor support for table calculations, large section of code for simple tasks

Support table calculation, good interactivity, training courses everywhere
Table calculation does not conform to natural thinking
Too many types of tables need to be mastered
The difficulty is far beyond non-professionals
df = pd.read_csv("../login_data.csv")
df["ts"] = pd.to_datetime(df["ts"]).dt.date
grouped = df.groupby("userid")
aligned_dates = pd.date_range(start=df["ts"].min(), end=df["ts"].max(), freq='D')
user_date_wether_con3days = []
for uid, group in grouped:
group = group.drop_duplicates('ts')
aligned_group = group.set_index("ts").reindex(aligned_dates)
consecutive_logins = aligned_group.rolling(window=7)
n = 0
date_wether_con3days = []
for r in consecutive_logins:
n += 1
if n<7:
continue
else:
ds = r['userid'].isna().cumsum()
cont_login_times = r.groupby(ds).userid.count().max()
wether_cont3days = 1 if cont_login_times>=3 else 0
date_wether_con3days.append(wether_cont3days)
user_date_wether_con3days.append(date_wether_con3days)
arr = np.array(user_date_wether_con3days)
day7_cont3num = np.sum(arr,axis=0)
result = pd.DataFrame({'dt':aligned_dates[6:],'cont3_num':day7_cont3num})
True set of records, with interactivity
Complex environment, cannot directly process desktop files, too hard for non-professionals to use
The complexity of procedural calculation is too high for non-professionals to master
WITH all_dates AS ( SELECT DISTINCT TRUNC(ts) AS login_date FROM login_data), user_login_counts AS ( SELECT userid, TRUNC(ts) AS login_date, (CASE WHEN COUNT(*)>=1 THEN 1 ELSE 0 END) AS login_count FROM login_data GROUP BY userid, TRUNC(ts)), whether_login AS ( SELECT u.userid, ad.login_date, NVL(ulc.login_count, 0) AS login_count FROM all_dates ad CROSS JOIN ( SELECT DISTINCT userid FROM login_data) u LEFT JOIN user_login_counts ulc ON u.userid = ulc.userid AND ad.login_date = ulc.login_date ORDER BY u.userid, ad.login_date), whether_login_rn AS ( SELECT userid,login_date,login_count,ROWNUM AS rn FROM whether_login), whether_eq AS( SELECT userid,login_date,login_count,rn, (CASE WHEN LAG(login_count,1) OVER (ORDER BY rn)= login_count AND login_count =1 AND LAG(userid,1) OVER (ORDER BY rn)=userid THEN 0 ELSE 1 END) AS wether_e FROM whether_login_rn ), numbered_sequence AS ( SELECT userid,login_date,login_count,rn, wether_e, SUM(wether_e) OVER (ORDER BY rn) AS lab FROM whether_eq), consecutive_logins_num AS ( SELECT userid,login_date,login_count,rn, wether_e,lab, (SELECT (CASE WHEN max(COUNT(*))<3 THEN 0 ELSE 1 END) FROM numbered_sequence b WHERE b.rn BETWEEN a.rn - 6 AND a.rn AND b.userid=a.userid GROUP BY b. lab) AS cnt FROM numbered_sequence a) SELECT login_date,SUM(cnt) AS cont3_num FROM consecutive_logins_num WHERE login_date>=(SELECT MIN(login_date) FROM all_dates)+6 GROUP BY login_date ORDER BY login_date;
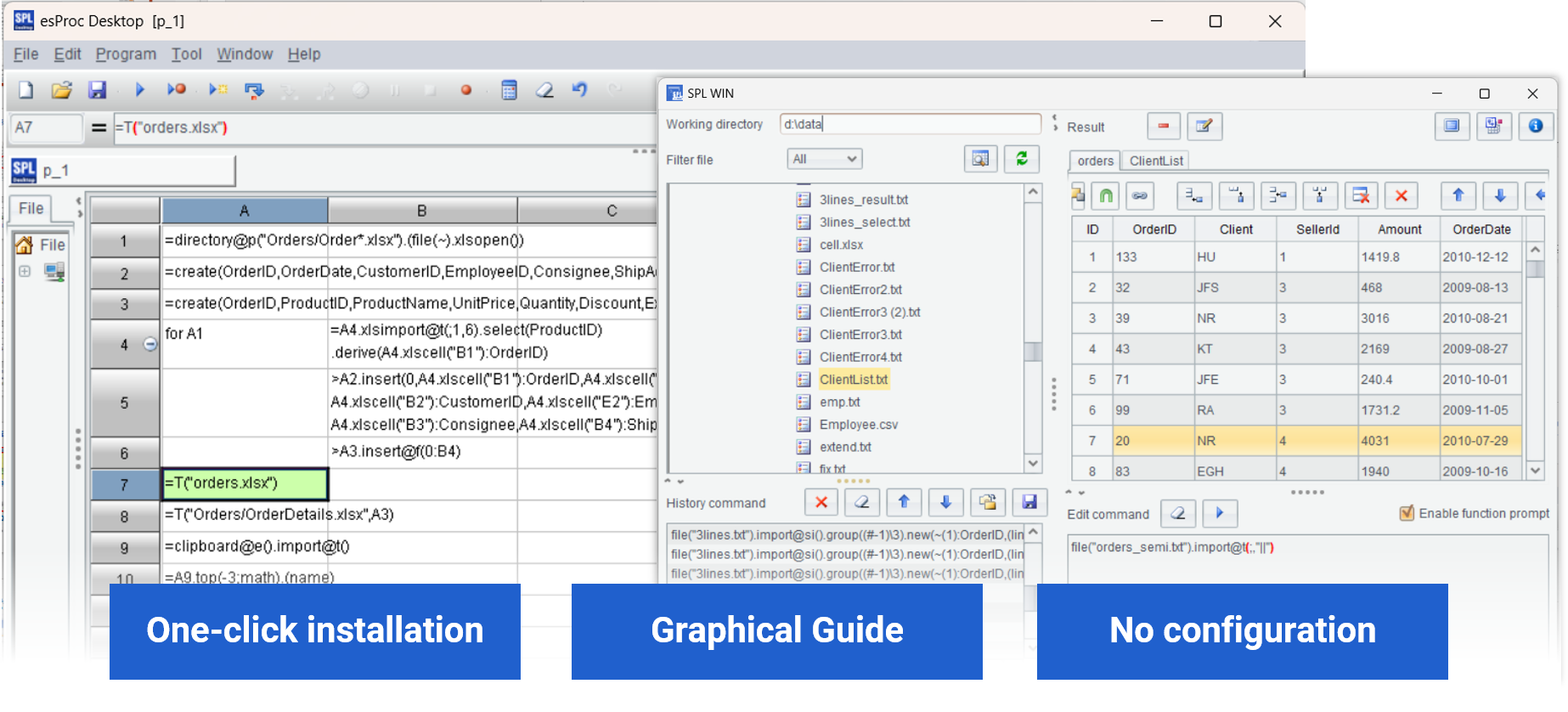
| A | |
| 1 | =file("login_data.csv").import@tc() |
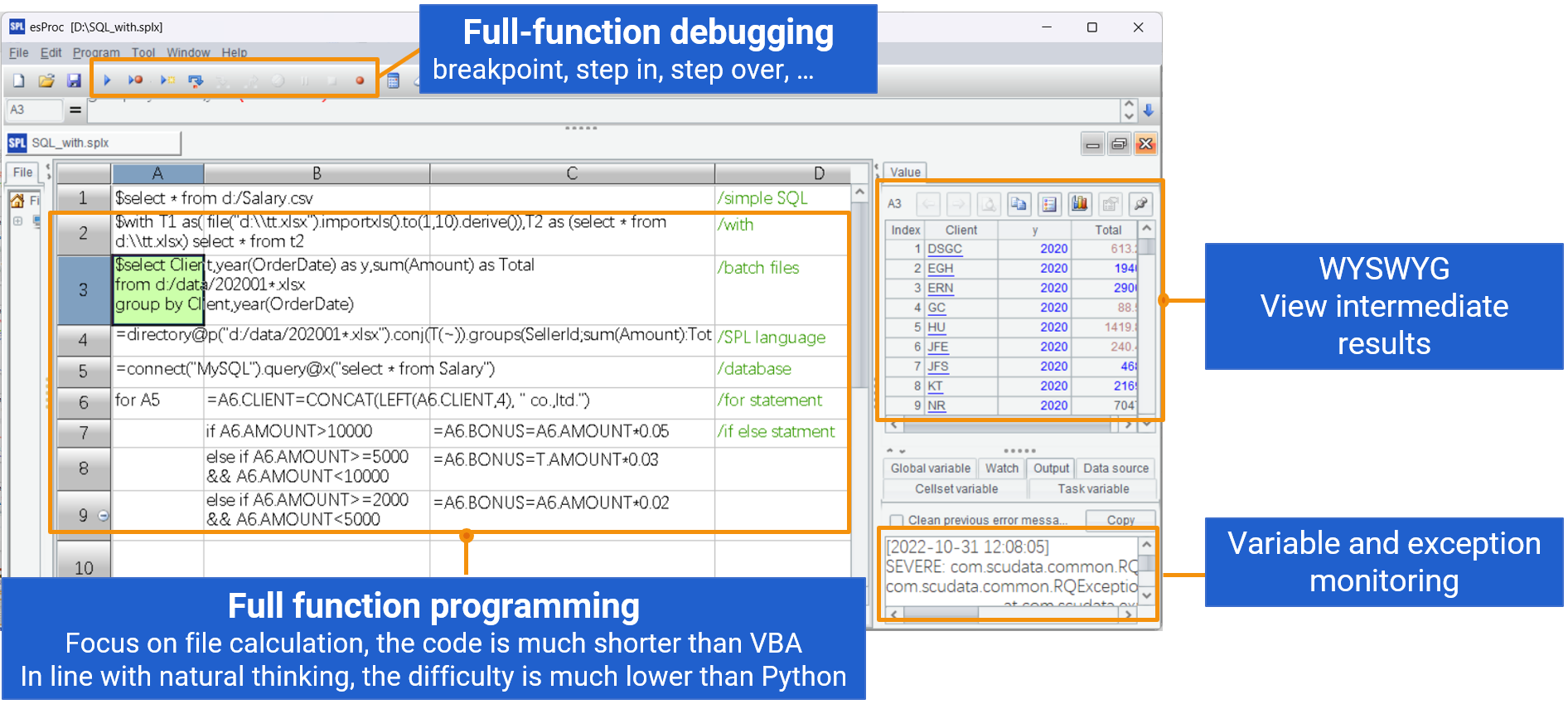
| 2 | =periods(date(A1.ts),date(A1.m(-1).ts)) |
| 3 | =A1.group(userid).(~.align(A2,date(ts)).(if(#<7,null,(cnt=~[-6:0].group@i(!~).max(count(~)),if(cnt>=3,1,0))))) |
| 4 | =msum(A3).~.new(A2(#):dt,int(~):cont3_num).to(7,) |

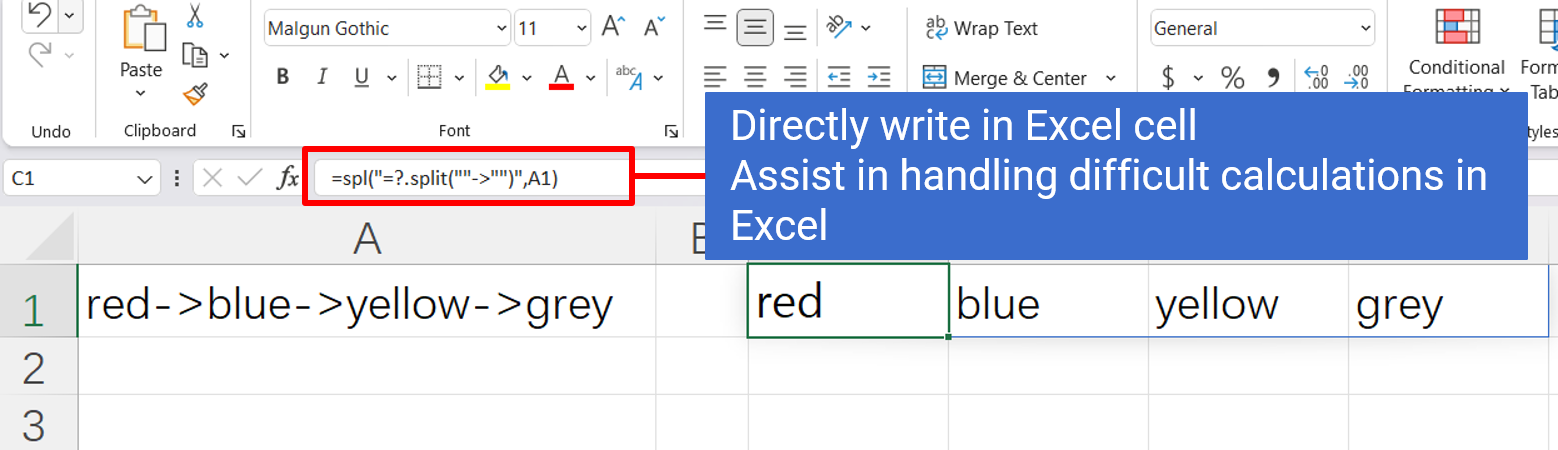
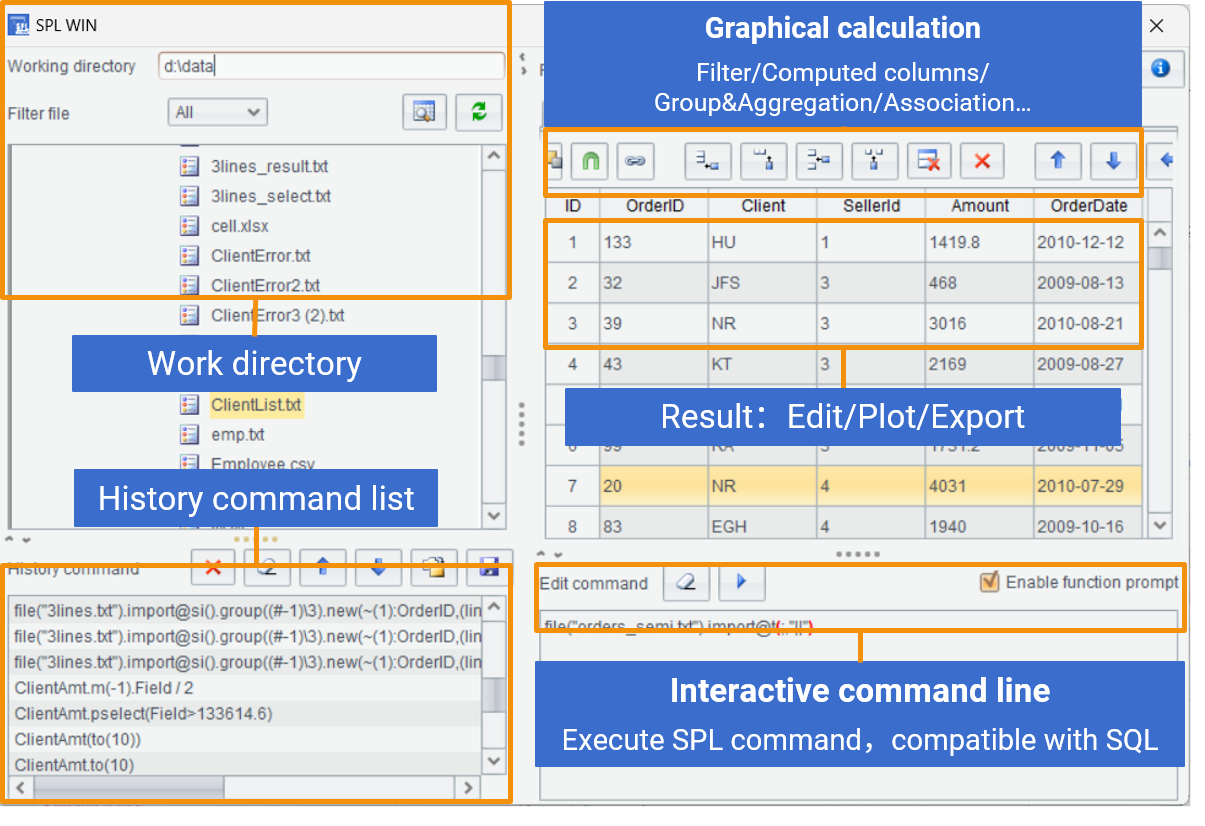





1. Group by model, month, year and count

2. Calculate YOY: if(Model==Model[-1] && Month==Month[-1],SalesVol/SalesVol[-1],null)

3. Resort by model, year, month

4. Calculate LRR: if(Model==Model[-1] ,SalesVol/SalesVol[-1],null)


1. Load 3 spreadsheets

2. Associate standard with absent and performance

3. Calculate wage according to the formula


| A | B | C | |
| 1 | =file("data.xlsx").xlsimport@t() | ||
| 2 | for A1.fname() | =A1.field(A2) | |
| 3 | =B2.sum() | =B2.sum(int(~)) | |
| 4 | =if(B3==C3,B2.mode(),B2.avg()) | ||
| 5 | =B2.(if(~,~,B4)) | >A1.field(A2,B5) | |
| 6 | >file("dataNew.xlsx").xlsexport@t(A1) | ||

| A | B | C | |
| 1 | [ID,Name,Sex,Postion,Birthday,Phone,Address,PostCode] | ||
| 2 | [C1,C2,F2,C3,C4,D5,C7,C8] | ||
| 3 | =directory@p("data/*.xlsx") | ||
| 4 | for A3 | =file(A4).xlsopen() | =B2.(B4.xlscell(~)) |
| 5 | =@|C4 | ||
| 6 | =create(${A1.concat@c()}).record(B5) | ||
| 7 | >file("all.xlsx").xlsexport@t(A6) | ||